- The Internet Protocol (IP) is the principal communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for Sending and receiving datagrams across network boundaries.
- Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet. IPv4 and IPv6 are the versions of IP.
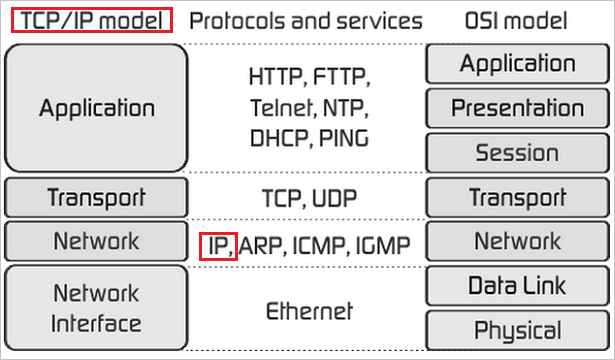
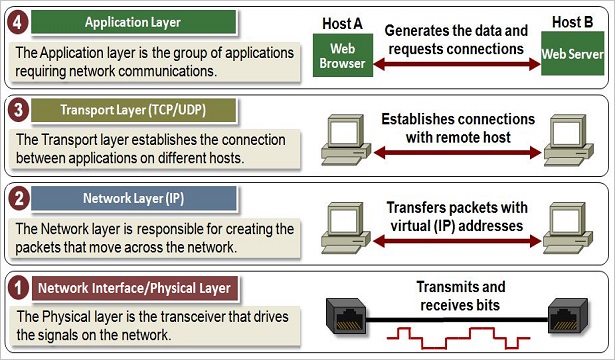
- The below figure shows the functionality of each TCP/IP model layers.
Why IP
- The Internet Protocol is responsible for addressing hosts and for routing datagrams (packets) from a source host to a destination host across one or more IP networks.
Datagram construction
- Each datagram has two components: a header and a payload. The IP header is tagged with the source IP address, the destination IP address, and other meta-data needed to route and deliver the datagram.
- The payload is the data that is transported. This method of nesting the data payload in a packet with a header is called encapsulation.
IP address
- An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
IP address classes
- With an IPv4 IP address, there are five classes of available IP ranges: Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D and Class E, while only A, B, and C are commonly used.
- Each class allows for a range of valid IP addresses, shown in the following table.
| Class | Address Range | Supports |
|---|---|---|
| Class A | 1.0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254 | Supports 16 million hosts on each of 127 networks. |
| Class B | 128.1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254 | Supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000 networks. |
| Class C | 192.0.1.1 to 223.255.254.254 | Supports 254 hosts on each of 2 million networks. |
| Class D | 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 | Reserved for multicast groups. |
| Class E | 240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254 | Reserved for future use, or Research and Development Purposes. |
IPv4 vs IPv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| Developed in 1974 by IETF. | Developed by IETF in 1998. |
| Ipv4 address is 32 bit. | IPv6 address is 128 bit. |
| Has issue with IP address depletion, due to Address shortage. | Has sufficient address to cater the needs of future as well. |
| IPv4 header is 20 bytes | IPv6 header is 40 bytes |
| IPv4 header has 13 fields and is more complicated. | IPv6 header has 8 fields and is less complicated to IPv4. |
| No Built-in Security mechanism. IP sec is optional. | Has Built-in Security : Encryption and Authentication. |
| Less suitable for Mobile networks. | Better Suited for Mobile networks. |
| IPv4 is still widely used. | IPv6 is picking up but still behind IPv4. |
| Packet flow is not identified. | Uses the Flow Label to identify the Packet Flow. |
| Number of addresses : 232 | Number of addresses : 2128 |
| Example of an IPv4 :10.10.10.10 | Example of IPv6 : FE80:0002:0000:0000:0102:A3EF:FE1F:8259 |


0 comments:
Post a Comment